Diabetes can significantly impact your feet, making them vulnerable to various conditions that, if left untreated, may lead to severe complications. Proper awareness of symptoms and timely treatment can help manage these issues effectively.
Common Diabetes-Related Foot Conditions
- Diabetic Neuropathy
High blood sugar levels can damage nerves in the feet, leading to diabetic neuropathy. Symptoms include numbness, tingling, and a reduced ability to feel pain or temperature changes, increasing the risk of unnoticed injuries. - Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Diabetes can cause poor blood circulation, particularly in the legs and feet. PAD may result in slow-healing wounds, infections, and even ulcers. Symptoms include leg pain, cramping, and a feeling of coldness in the feet. - Foot Ulcers
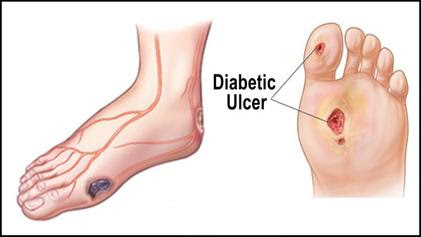
Open sores or ulcers are common in diabetic patients, often caused by minor injuries or pressure points. If neglected, these can become infected and lead to complications. - Infections
Even minor cuts or blisters can turn into severe infections in diabetic feet due to poor circulation and immunity. - Charcot Foot
This condition causes weakening of the bones in the foot, leading to deformities. It often begins with redness, warmth, and swelling.
Symptoms to Watch For
- Persistent pain or swelling
- Changes in skin color or temperature
- Sores, cuts, or blisters that don’t heal
- Foul-smelling discharge from a wound
- Numbness or tingling in the feet
Treatment Options
- Regular Foot Care
Keep your feet clean, moisturized, and inspect them daily for any injuries. Trim toenails carefully to avoid ingrown nails. - Wound Management
For foot ulcers or wounds, seek medical attention immediately. Treatment may include cleaning, dressing, and sometimes antibiotics. - Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing and managing foot conditions. - Specialized Footwear
Wear diabetic-friendly shoes to reduce pressure points and prevent injuries. - Surgical Intervention
In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove infected tissue, correct deformities, or restore circulation.
Preventive Measures
- Regular check-ups with a podiatrist or foot specialist
- Avoid walking barefoot
- Stay active to improve circulation
- Quit smoking, as it worsens blood circulation
Timely diagnosis and proper care can prevent diabetes-related foot complications. If you experience any unusual symptoms, consult a diabetic foot ulcer specialist immediately.
By prioritizing foot health, diabetic individuals can lead a healthier, complication-free life.

