ANKLE SPRAIN
What is Ankle Sprain?
Ankle Sprain is a common injury that occurs when the ligaments supporting the ankle are stretched or torn, usually due to sudden twisting, rolling, or turning of the foot. It can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the ligament damage.
Without proper treatment and rehabilitation, even a minor ankle sprain can lead to long-term weakness, instability, or repeated injuries.
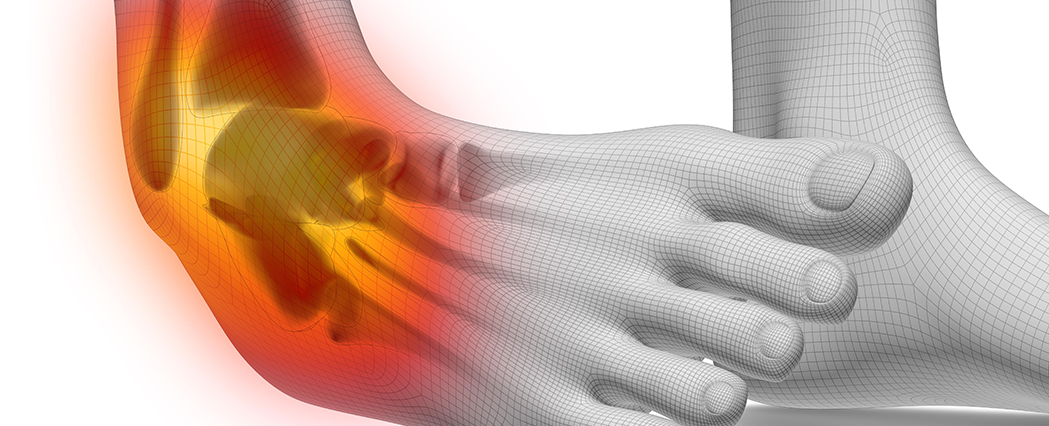
Common Symptoms of Ankle Sprain
Ankle sprain symptoms may vary based on severity but typically include:
Sudden pain in the ankle after twisting or turning it
Swelling and tenderness around the ankle joint
Bruising or discoloration
Difficulty bearing weight or walking
A popping sound or sensation at the time of injury
Stiffness or limited range of motion
What Causes an Ankle Sprain?
Ankle sprains are usually caused by:
Sudden twisting, rolling, or turning of the foot
Stepping on uneven surfaces or missing a step
Sports injuries involving jumping, pivoting, or quick directional changes
Weak ankles due to previous injuries
Improper footwear during physical activity
Most ankle sprains involve the lateral ligaments (on the outside of the ankle), but medial or high ankle sprains can also occur.
Ankle Sprain Diagnosis
A proper diagnosis ensures effective treatment and faster recovery, especially since a sprain may sometimes be mistaken for a fracture. That’s why medical evaluation is crucial. A doctor treating an ankle sprain will begin with a thorough physical examination to check for swelling, bruising, and any signs of instability. They will assess ligament tenderness and test the ankle’s range of motion to evaluate the extent of the injury. Stress tests may be used to determine the degree of ligament damage. To rule out any fractures, X-rays are often recommended. If a ligament tear or joint damage is suspected, the doctor may also advise an MRI or ultrasound for a more detailed view.
Ankle Sprain Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity of the sprain—Grade I (mild), Grade II (moderate), or Grade III (severe ligament tear).
Initial Care (RICE Protocol):
Rest: Avoid putting weight on the injured ankle
Ice: Apply ice packs to reduce swelling
Compression: Use elastic bandages or ankle braces
Elevation: Raise the foot above heart level
Medical Treatment:
Pain relief using anti-inflammatory medications
Immobilization with braces or splints for moderate to severe sprains
Crutches if weight-bearing is painful
Physiotherapy to regain strength, flexibility, and balance
Rehabilitation exercises to prevent future sprains
When to See a Doctor for Ankle Sprain
Consult a doctor if you experience:
Severe swelling or bruising
Inability to walk or bear weight
Pain that doesn’t improve with home care in 2–3 days
Recurring ankle sprains
Feeling of instability or “giving way” in the ankle
Advanced or Surgical Options
In rare cases of complete ligament rupture or recurring instability, surgery may be required. Surgical options include:
Ligament repair or reconstruction
Arthroscopy to remove loose fragments
Tendon grafting for severe damage
Dr. Shakti Swaroop ensures surgery is considered only when absolutely necessary and focuses on conservative recovery wherever possible.
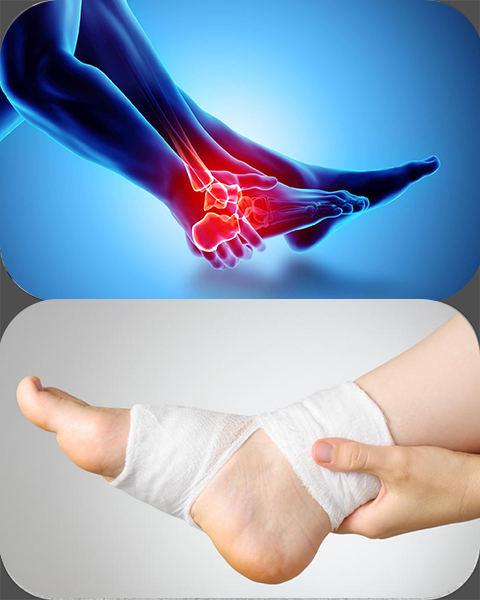
Get Expert Ankle Sprain Treatment
Whether it’s a sports injury or a sudden twist during daily movement, ankle sprains need the right treatment and rehab to avoid long-term complications. Dr. Shakti Swaroop and his team offer comprehensive care—from initial diagnosis to complete rehabilitation.
📞 Book your consultation today for specialized ankle sprain treatment in Bhubaneswar.
frequently
asked questions
A sprained ankle usually causes pain, swelling, and bruising but allows limited movement. A broken ankle may cause intense pain, inability to move or bear weight, and visible deformity. X-rays are needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Yes, Grade I sprains often heal with rest, ice, compression, and elevation. However, it’s important to follow up with a doctor to ensure proper recovery and avoid future sprains.
Recovery time varies:
Grade I: 1–2 weeks
Grade II: 3–6 weeks
Grade III: 8 weeks or longer
Physiotherapy may be needed for full functional recovery.
Untreated sprains can lead to chronic instability, joint stiffness, recurrent sprains, or even arthritis over time. Early treatment ensures proper ligament healing and reduces the risk of complications.
For personalized and expert ankle sprain treatment in Bhubaneswar, consult Dr. Shakti Swaroop. He offers advanced diagnostics, tailored rehabilitation plans, and conservative to surgical care options as needed.
